Spring Contrainer & Bean
1) 스프링 컨테이너의 개념
스프링 프레임워크에서 객체(Bean)를 생성, 배포, 관리하기위해
커다란 박스를 만드는데 그것을 스프링 컨테이너라고 합니다.

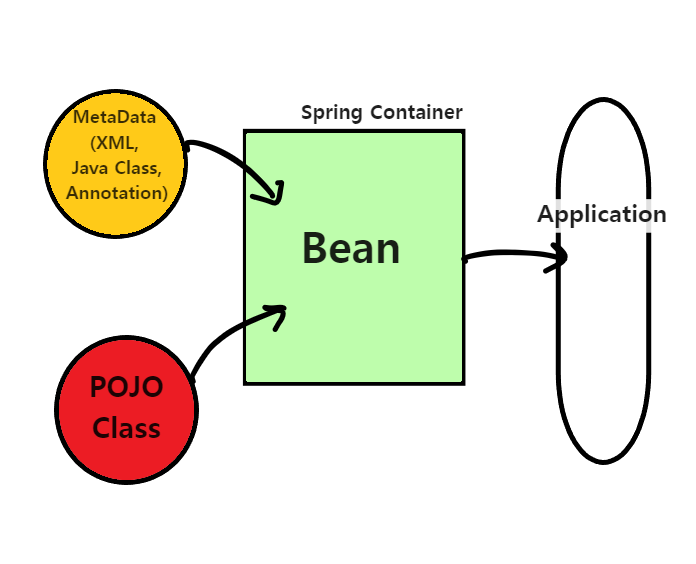
2) Bean의 개념
스프링 프레임워크에서 관리되는 객체를 의미합니다.
Bean은 크게 두가지로 나눌 수 있다.
일반적인 Java 클래스로서 특정한 인터페이스를 구현하거나 클래스를 상속받을 필요가 없습니다.
스프링에서는 POJO 클래스를 Bean으로 인식하고 스프링 컨테이너에 등록할 수 있습니다.
메타데이터는 XML, Annotation 또는 JavaConfig 형식으로 작성될 수 있습니다.
메타데이터는 Bean의 속성, 의존성, 라이프사이클 등을 정의하고,
스프링 컨테이너는 해당 메타데이터를 기반으로 Bean을 생성 및 관리합니다.
3) 그럼 스프링 컨테이너를 왜 사용할까?
스프링 컨테이너는 아래와 같은 장점이 있기 때문에 사용합니다.
① 의존성 관리
Spring 컨테이너는 객체 간의 의존성을 관리해줍니다.
객체 간의 의존성을 주입(Dependency Injection)을 통해 해결하므로,
개발자는 객체 생성 및 의존성 주입에 대한 로직을 직접 작성할 필요가 없습니다.
② 라이프사이클 관리
Bean의 라이프사이클을 관리해줍니다.
이를 활용하면 초기화, 소멸 등의 작업을 명시적으로 처리할 필요 없이 스프링 컨테이너가 자동으로 처리합니다.
개발자는 Bean의 초기화와 소멸에 집중하는 대신 핵심 비즈니스 로직에 더 많은 시간과 노력을 투자할 수 있습니다.
③ AOP 지원
관점 지향 프로그래밍(AOP)을 지원합니다.
AOP를 사용하여 로깅, 트랜잭션 관리, 보안 등과 같은 부가적인 기능을 애플리케이션에 적용할 수 있습니다.
④ 테스트 용이성
의존성 주입을 통해 모듈 간의 결합도가 낮아지므로, 단위 테스트나 통합 테스트 등을 쉽게 작성할 수 있습니다.
4) 스프링 컨테이너의 종류
| ApplicationContext | WebApplicationContext | |
| 용도 | 일반적인 스프링 애플리케이션 | 웹 기반 스프링 애플리케이션 |
| 주요 기능 | DI(Dependency Injection) AOP(Aspect-Oriented Programming) 빈 관리 등 |
DI(Dependency Injection) AOP(Aspect-Oriented Programming) 빈 관리, 웹 기능 등 |
| 환경 설정 | XML, JavaConfig, Annotation 등 | XML, JavaConfig, Annotation 등 |
| 웹 관련 기능 | 지원하지 않음 | 웹 애플리케이션 컨텍스트 설정, 웹 환경 관련 기능 지원 |
| 주요 인터페이스 | ApplicationContext | WebApplicationContext, ConfigurableWebApplicationContext |
| 서블릿 컨텍스트 지원 |
지원 X | 서블릿 컨텍스트 설정, 서블릿 환경 관련 기능 지원 |
| 장점 | 다양한 설정 방식 지원 일반적인 스프링 애플리케이션에 적합 |
웹 애플리케이션에 특화된 기능 지원 서블릿 컨텍스트 설정 가능 |
| 단점 | 웹 관련 기능 지원하지 않음 서블릿 컨텍스트 설정 불가능 |
웹 애플리케이션에 특화된 기능이므로 일반적인 스프링 애플리케이션에 비효율적 |
5) 스프링 컨테이너 동작순서

① 설정 정보 작성
스프링 애플리케이션의 설정 정보를 작성합니다.
설정 정보는 XML, 애노테이션 또는 JavaConfig 형식으로 작성될 수 있습니다.
설정 정보는 스프링 컨테이너에게 Bean을 생성하고 구성하는 방법을 알려줍니다.
② 컨테이너 생성
설정 정보를 기반으로 스프링 컨테이너를 생성합니다.
스프링 컨테이너는 설정 정보를 읽고 Bean을 생성하고 관리하는 역할을 수행합니다.
③ Bean 정의
스프링 컨테이너는 설정 정보에 따라 Bean을 정의합니다.
이 때 Bean의 Configuration Metadata (Class, Name, Property 등)을 정의합니다.
※ Bean의 Configuration Metadata
| Metadata | 설명 |
| class | Bean이 생성될 때 사용될 클래스의 전체 경로를 포함한 패키지명과 클래스명입니다. |
| name | Bean의 이름입니다. 고유한 식별자로 사용되며, 문자열 형태로 정의됩니다. |
| scope | Bean의 인스턴스를 생성하고 관리하는 범위를 지정합니다. Singleton, Prototype 등을 선택할 수 있습니다. |
| property | Bean이 가지는 속성을 설정합니다. 주로 프로퍼티(property)라고 불리며, Bean 내부의 필드에 값을 주입하거나 가져올 때 사용됩니다. |
| constructor-arg | Bean의 생성자에 전달되는 인자 값을 설정합니다. 주로 다른 Bean이나 값을 전달합니다. |
| autowiring mode |
Bean 간의 의존성 주입을 자동으로 처리하는 방식을 설정합니다. 주로 byName, byType, constructor 등의 모드를 선택할 수 있습니다. |
| lazy-initialization mode |
Bean의 지연 초기화 모드를 설정합니다. Bean이 처음 사용될 때 생성되도록 할지, 필요할 때까지 생성을 지연할지를 정합니다. |
| initialization method |
Bean의 초기화를 위한 메서드를 지정합니다. Bean이 생성된 후에 실행됩니다. |
| destruction method |
Bean의 소멸을 위한 메서드를 지정합니다. Bean이 제거되기 전에 실행됩니다. |
④ Bean 생성
스프링 컨테이너는 Bean의 정의를 바탕으로 Bean의 인스턴스를 생성합니다.
⑤ 의존성 주입
Bean 생성 후, 스프링 컨테이너는 의존성 주입(Dependency Injection)을 수행합니다.
의존성 주입은 Bean이 필요로 하는 다른 Bean을 찾아서 해당 Bean을 주입하는 작업을 의미합니다.
⑥ 초기화
Bean이 생성되고 의존성이 주입된 후, 스프링 컨테이너는 Bean의 초기화 작업을 수행합니다.
초기화 작업은 커스텀한 초기화 메서드를 호출하거나 특정 인터페이스를 구현한 메서드를 실행하는 등의 방식으로 !
⑦ Bean의 사용
Bean이 초기화된 후, 스프링 컨테이너나 애플리케이션에서 해당 Bean을 사용할 수 있습니다.
Bean은 필요한 시점에 컨테이너로부터 요청되거나, 애플리케이션에서 필요한 곳에서 직접 참조될 수 있습니다.
⑧ 소멸
스프링 컨테이너가 종료될 때 또는 필요한 경우에 Bean의 소멸 작업을 수행합니다.
소멸 작업은 커스텀한 소멸 메서드를 호출하거나 특정 인터페이스를 구현한 메서드를 실행하는 등의 방식으로 !
6) Bean의 설정 방식에 따른 예시
① XML 방식 + ApplicationContext 컨테이너
com.example.Pokemon.java
public class Pokemon {
private String name;
private String type;
private int level;
public Pokemon() {
}
public void attack() {
System.out.println(name + "이(가) 공격합니다!");
}
// Getter와 Setter 메서드는 생략되었습니다.
}
PokemonConfig.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 포켓몬 Pikachu 빈 정의 -->
<bean id="pikachu" class="com.example.Pokemon">
<property name="name" value="Pikachu" />
<property name="type" value="Electric" />
<property name="level" value="50" />
</bean>
</beans>이름(name), 타입(type), 레벨(level) 속성을 초기화
Main.java
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("PokemonConfig.xml");
Pokemon pikachu = (Pokemon) context.getBean("pikachu");
pikachu.attack();
((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext) context).close();
}
}"PokemonConfig.xml"이라는 파일을 Classpath에서 찾아서 스프링 컨테이너를 형성하고,
그 결과를 ApplicationContext 타입의 context 변수에 할당하는 것을 의미합니다.
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 클래스는 XML 파일을 로드하여 스프링 컨테이너를 초기화하는 역할을 수행합니다.
② XML 방식 + WebApplicationContext 컨테이너
com.example.Pokemon.java
public class Pokemon {
private String name;
private String type;
private int level;
public Pokemon() {
}
public void attack() {
System.out.println(name + "이(가) 공격합니다!");
}
// Getter와 Setter 메서드는 생략되었습니다.
}
PokemonConfig.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- WebApplicationContext 설정 -->
<context:annotation-config />
<context:component-scan base-package="com.example" />
<!-- 포켓몬 Pikachu 빈 정의 -->
<bean id="pikachu" class="com.example.Pokemon">
<property name="name" value="Pikachu" />
<property name="type" value="Electric" />
<property name="level" value="50" />
</bean>
</beans>
● <context:annotation-config />
Annotation을 사용하여 자동 구성을 활성화합니다.
● <context:component-scan base-package="com.example" />
com.example 패키지를 기준으로 자동으로 컴포넌트 스캔을 수행합니다.
해당 패키지와 하위 패키지에 있는 클래스 중에서 스프링 관련 Annotation이 지정된 클래스를 찾아 빈으로 등록합니다.
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<display-name>MyWebApp</display-name>
<!-- Spring WebApplicationContext 설정 -->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/PokemonConfig.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/spring-mvc-config.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
● <context-param>
context-param은 웹 애플리케이션의 전체 범위에서 사용되는 매개변수를 정의하고 설정하는 데 사용됩니다.
contextConfigLocation이라는 컨텍스트 매개변수를 설정하고 있습니다.
이 매개변수는 스프링 컨텍스트 설정 파일의 경로를 지정합니다.
여기서는 /WEB-INF/PokemonConfig.xml 파일을 지정하여 스프링 컨텍스트 설정을 포함하고 있습니다.
● <listener>
Java 웹 애플리케이션에서 이벤트를 수신하고 처리하는 객체입니다.
웹 애플리케이션에서 발생하는 다양한 이벤트(예: 서블릿 생명주기 이벤트, 세션 이벤트, 컨텍스트 이벤트 등)를 감지하고 필요한 작업을 수행할 수 있도록 해줍니다.
위의 예시에서는 org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener 클래스를 리스너로 등록하고 있습니다.
이를 통해 스프링의 ApplicationContext가 웹 애플리케이션의 컨텍스트 로딩 및 초기화 시에 생성되고 설정됩니다.
* ContextLoaderListener 클래스는 스프링 프레임워크에서 제공하는 클래스로, 스프링 웹 애플리케이션의 컨텍스트 로딩과 초기화를 처리하기 위해 사용됩니다. 따라서 이 클래스는 스프링 라이브러리에 포함되어 있으며, 우리가 따로 선언해주지 않아도 사용할 수 있습니다.
Main.java
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new XmlWebApplicationContext();
((XmlWebApplicationContext) context).setConfigLocation("/WEB-INF/PokemonConfig.xml");
((XmlWebApplicationContext) context).refresh();
Pokemon pikachu = (Pokemon) context.getBean("pikachu");
pikachu.attack();
((XmlWebApplicationContext) context).close();
}
}
● ((XmlWebApplicationContext) context).setConfigLocation("/WEB-INF/PokemonConfig.xml");
context 객체를 XmlWebApplicationContext 타입으로 캐스팅한 후,
setConfigLocation 메서드를 호출하여 설정 파일의 위치를 지정합니다.
여기서는 "/WEB-INF/PokemonConfig.xml" 경로를 설정 파일로 사용합니다.
● ((XmlWebApplicationContext) context).refresh();
context 객체를 XmlWebApplicationContext 타입으로 캐스팅한 후, refresh 메서드를 호출하여 컨텍스트를 초기화합니다. 이때, 설정 파일을 기반으로 빈의 생성과 초기화 작업이 수행됩니다.
※ 타입 변환한 이유
ApplicationContext 인터페이스에는 setConfigLocation() 및 refresh()와 같은 특정 메서드가 직접 정의되어 있지 않지만 ApplicationContext 인터페이스를 구현한 구체적인 클래스(XmlWebApplication)에는 이러한 메서드가 구현되어 있습니다.
XmlWebApplicationContext는 setConfigLocation() 및 refresh()와 같은 메서드를 구현하여
XML 설정 파일의 위치를 설정하고 컨텍스트를 초기화합니다.
따라서 Main.java 코드에서 XmlWebApplicationContext로 타입 캐스팅을 하는 것은
XmlWebApplicationContext의 특정 기능을 사용하기 위한 것입니다.
③ Java Class 방식
Pokemon.java
public class Pokemon {
private String name;
private String type;
private int level;
public Pokemon() {
}
public void attack() {
System.out.println(name + "이(가) 공격합니다!");
}
// Getter와 Setter 메서드는 생략되었습니다.
}
AppConfig.java
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public Pokemon pikachu() {
Pokemon pikachu = new Pokemon();
pikachu.setName("Pikachu");
pikachu.setType("Electric");
pikachu.setLevel(50);
return pikachu;
}
}
● @Configuration
이 클래스가 스프링의 구성(Configuration) 클래스임을 나타냅니다.
스프링 컨테이너에게 해당 클래스가 구성 요소를 정의하는 역할을 한다는 것을 알려줍니다.
● @Bean
해당 메서드가 스프링 컨테이너에 의해 관리되는 빈(Bean)을 생성하는 메서드임을 나타냅니다.
pikachu() 메서드는 Pokemon 객체를 생성하고 반환합니다.
● return pikachu;
생성된 Pokemon 객체를 반환합니다. 이 객체는 스프링 컨테이너에 의해 관리되는 빈으로 등록됩니다.
Main.java
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
Pokemon pikachu = context.getBean("pikachu", Pokemon.class);
pikachu.attack();
((AnnotationConfigApplicationContext) context).close();
}
}
● ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext를 사용하여 AppConfig 클래스에 정의된 스프링 빈(Bean) 설정 정보를 기반으로
애플리케이션 컨텍스트를 생성하고, 이를 context 변수에 할당하는 역할을 합니다.
● Pokemon pikachu = context.getBean("pikachu", Pokemon.class);
Java 클래스 형식으로 getBean()을 호출할 때는 getBean("가져올 빈 객체 이름", 클래스.class)와 같은 형식을 사용합니다.
애플리케이션 컨텍스트에서 이름이 "pikachu"인 빈(Bean)을 가져와서
Pokemon 타입으로 변환하여 pikachu 변수에 할당하는 코드입니다.
④ Annotation 설정 방식
Pokemon.java
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Pokemon {
private String name;
private String type;
private int level;
public Pokemon() {
}
public void attack() {
System.out.println(name + "이(가) 공격합니다!");
}
// Getter와 Setter 메서드는 생략되었습니다.
}
● @Component
해당 클래스를 스프링의 빈(Bean)으로 등록하는데 사용되는 Annotation입니다.
@Component Annotation을 사용하면 스프링 컨테이너가 자동으로 이 클래스의 인스턴스를 생성하고 관리합니다.
PokemonRepository.java
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class PokemonRepository {
public void save(Pokemon pokemon) {
// 포켓몬 정보를 저장하는 로직
System.out.println(pokemon.getName() + " 정보를 저장했습니다.");
}
}
● @Repository
Repository Annotation은 스프링 프레임워크에서 Repository(데이터 액세스 객체)로 사용되는 클래스에 붙이는 Annotation입니다. 스프링 컨테이너에게 이 클래스가 데이터 액세스 관련 기능을 제공하는 클래스임을 알려줍니다.
● public void save(Pokemon pokemon) {
save 메서드를 정의합니다. 이 메서드는 Pokemon 객체를 인자로 받아서 포켓몬 정보를 저장하는 로직을 수행합니다.
※ Repository 와 Component의 차이
| @Repository | @Component | |
| 목적 | 데이터 액세스 계층의 구성 요소 | 일반적인 구성 요소 |
| 예상되는 용도 |
데이터베이스 액세스, 예외 처리 등 | 비즈니스 로직, 유틸리티, 컨트롤러 |
| 스프링 예외 변환 |
예외를 스프링의 DataAccessException으로 변환합니다. |
예외를 변환하지 않습니다. |
| 롤백 트랜잭션 관리 |
롤백 트랜잭션을 자동으로 관리합니다. | 롤백 트랜잭션을 자동으로 관리하지 않습니다. |
| 추가적인 기능 제공 |
Spring Data JPA와 통합 가능합니다. | 추가적인 기능을 제공하지 않습니다. |
● 데이터 액세스 계층 : Repository, DAO, Entity, Mapper 등
● 일반적인 구성요소 : Service, Controller, Utility(재사용가능한 클래스나 메소드), Helper 등
PokemonService.java
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class PokemonService {
private final PokemonRepository pokemonRepository;
@Autowired
public PokemonService(PokemonRepository pokemonRepository) {
this.pokemonRepository = pokemonRepository;
}
public void savePokemon(Pokemon pokemon) {
pokemonRepository.save(pokemon);
}
}
● @Service
Service Annotation은 해당 클래스가 서비스 계층의 빈으로 등록됨을 나타냅니다.
● @Autowired
생성자에 @Autowired 어노테이션을 사용하여 의존성 주입을 수행합니다.
이는 PokemonRepository 타입의 빈을 주입받아 pokemonRepository 변수에 할당합니다.
● public void savePokemon(Pokemon pokemon) {
pokemonRepository.save(pokemon); } }
savePokemon 메서드를 정의합니다.
이 메서드는 Pokemon 객체를 파라미터로 받아 pokemonRepository의 save 메서드를 호출하여
Pokemon 정보를 저장합니다.
※ 헷갈리지 않게 1
● public PokemonService(A B){ this.C = D; }
A 타입의 객체인 B가 생성자의 파라미터*로 전달되고,.
생성자 내부에서 C라는 A 타입의 멤버 변수에 D라는 B 객체가 할당됩니다.
* 파라미터 : 메서드나 생성자에 전달되는 값으로, 해당 메서드 또는 생성자 내에서 사용되는 변수
● public PokemonService(PokemonRepository pokemonRepository) {
this.pokemonRepository = pokemonRepository;
}
PokemonRepository(A) 타입의 객체인 pokemonRepository(B)가 생성자의 파라미터로 전달되고,
생성자 내부에서 pokemonRepository(C)라는 PokemonRepository(A) 타입의 멤버 변수에
pokemonRepository(D)라는 pokemonRepository(B)객체가 할당됩니다.
※ 헷갈리지 않게 2
● public void savePokemon(A B) { pokemonRepository.save(C); }
A 타입의 객체인 B가 savePokemon 메서드의 파라미터로 전달됩니다.
pokemonRepository의 save 메서드에 C가 전달됩니다. (B = C)
●public void savePokemon(Pokemon pokemon) {
pokemonRepository.save(pokemon); } }
Pokemon 객체가 savePokemon 메서드의 파라미터로 전달되고,
이 객체가 pokemonRepository.save() 메서드를 호출하여 저장됩니다.
Main.java
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
context.scan("com.example"); // 패키지 스캔을 통해 컴포넌트를 찾음
context.refresh();
Pokemon pikachu = new Pokemon();
pikachu.setName("Pikachu");
pikachu.setType("Electric");
pikachu.setLevel(50);
PokemonService pokemonService = context.getBean(PokemonService.class);
pokemonService.savePokemon(pikachu);
context.close();
}
}
● AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 클래스의 인스턴스인 context를 생성합니다.
● context.scan("com.example");
context에서 scan 메서드를 사용하여 "com.example" 패키지를 스캔하고, 컴포넌트를 찾습니다.
● context.refresh();
context에서 refresh 메서드를 호출하여 컨텍스트를 새로 고칩니다.
⑤ Bean 설정 방식에 따른 장단점
| Java 클래스 방식 | 어노테이션 설정 방식 | XML 방식 | |
| 장점 | 타입 안정성이 높고 컴파일 시 오류를 잡을 수 있음 | 간결하고 가독성이 좋음 | 설정이 외부화되어 유지 보수 및 관리가 용이 |
| 컴포넌트 스캔과 어노테이션 활용으로 설정이 간편 | 자바 어노테이션을 통해 설정을 명시적으로 표현 | 설정 변경 시 애플리케이션을 재시작하지 않아도 됨 | |
| 리팩토링 시 리팩토링 대상 클래스만 수정하면 됨 | 컴포넌트 스캔을 통한 자동 등록 및 주입 지원 | XML 구성 파일을 통해 유연한 설정이 가능 | |
| 단점 | 수정이 필요한 경우 컴파일 및 재배포가 필요 | 어노테이션의 오용으로 인한 오버헤드 가능성 | XML 구성 파일의 복잡성과 가독성 저하 |
| 설정 클래스의 크기가 커질 수 있음 | 어노테이션 사용을 위한 학습 곡선 존재 | 타입 안정성이 떨어질 수 있음 | |
| 의존성 주입이 복잡해질 수 있음 |
2023.06.28 - [Spring] - 의존성 역전 (IoC, Inversion of Control)
의존성 역전 (IoC, Inversion of Control)
의존성 역전 1) 의존성 역전(IoC, Inversion of Control)의 개념 소프트웨어 개발에서 컴퓨터 프로그램의 제어 흐름을 역전시키는 개념 일반적으로 프로그램의 제어 흐름은 개발자가 코드를 작성하여
devwarriorjungi.tistory.com
'Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Spring] Pageable과 PageRequest 개념과 비교 (0) | 2023.07.19 |
|---|---|
| [Spring] Spring MVC 구조 (0) | 2023.06.30 |
| [Spring] 의존성 역전 (IoC, Inversion of Control) (0) | 2023.06.28 |
| [Spring] 의존성주입(DI, Dependency Injection) (0) | 2023.06.27 |
| [Spring] Spring의 개념과 기원 (0) | 2023.06.27 |
